What Is Sickle Cell Disease?
Sickle cell disease is a hereditary blood disease. People with sickle cell disease have red blood cells, shaped like a sickle (hence the name of the disease) instead of a donut. Sickle cells have a shorter lifespan, and therefore lead to anemia. In addition, the sickle cells obstruct the blood vessels, and do so when provoked by fever or infection, pain, dehydration, cold, stress or fatigue.
Symptoms
People with sickle cell disease are always tired due to the severe anemia they have and experience painful sickle cell crises periodically. These painful episodes often require hospital admissions for intravenous fluids and a morphine infusion.
The obstruction of blood vessels causes damage to all organs such as kidneys, brain and lungs. People with sickle cell disease die too young. In the Netherlands on average about 30 years earlier than
a healthy individual.
Numbers
The total number of people with sickle cell disease in the Netherlands is estimated at 2000. Half of these are children.
Every year, 60 new patients are born in the Netherlands. In the Netherlands, due to the severity of the disease, newborns are tested for sickle cell disease immediately after birth during the national neonatal screening. A baby with sickle cell disease is referred to a Sickle Cell Comprehensive Care Center. It is important for parents to know that their child needs extra care and medication. Especially in childhood, there is an increased risk of serious infections if the child does not receive daily antibiotics and additional vaccinations.
More than
30 million
people worldwide suffer from sickle cell disease
Every year,
300.000
babies with sicklecell disease are born
In the Netherlands,
2.000
are known to be affected with sickle cell disease
Where did the disease originally arise?
Protection for Malaria
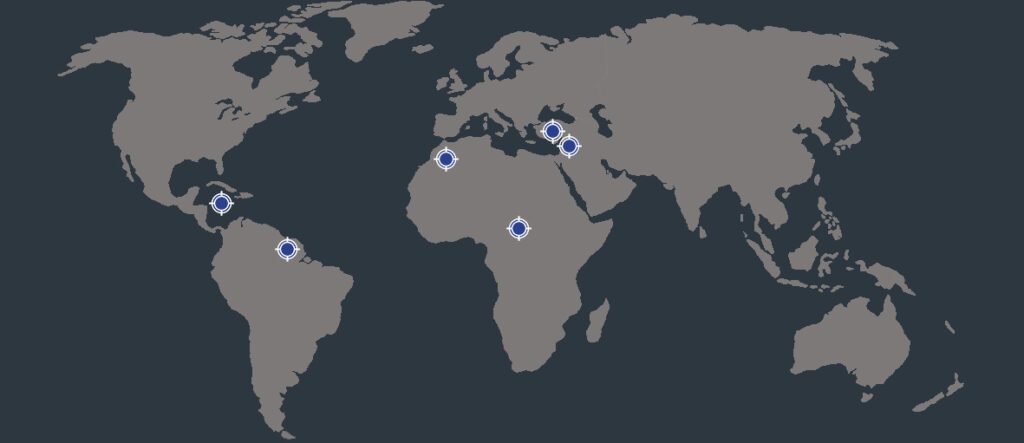
The disease originally evolved in the regions around the equator, because people who were carriers of sickle cell disease were better protected against malaria.
Due to migration, the disease now occurs all over the world.
In the Netherlands, especially in people from Suriname, the Caribbean, Central Africa, Morocco, Turkey and Syria.
Carriership of sickle cell disease occurs at average in one in seven people (15%). Both men and women can be carriers of sickle cell disease.
Hereditary
Sickle cell disease is a hereditary blood disease that is passed from parents to their child. When both parents are carriers of the disease, every pregnancy there is a 25% chance that the child will be affected with sickle cell disease.
Living with sickle cell disease
The impact of sickle cell disease on daily life is enormous due to the severe anemia, painful episodes and overall organ damage. Everything revolves around the disease for the patient and their family: both physically and mentally.
Children miss a lot of school and contact with friends.
It is difficult for adults to follow their schooling and to find suitable work. Due to the lack of awareness and knowledge of the disease, patients receive little understanding from their environment and therefore often feel that they are excluded from society.
Sign up for our newsletter and become a friend of the Dutch Sickle Cell Foundation!
The newsletter is sent once or twice a year.
